RemoteKeyBorg - Control your PicoBorg car remotely with the keyboard
Want to be able to control your PicoBorg from another Raspberry Pi or computer, then you want RemoteKeyBorg!
RemoteKeyBorg is a pair of scripts that allow a Raspberry Pi with a PicoBorg to expose itself on the network and another to command it.
This example is intended to demonstrate using the keyboard left, up, and right keys to control a three wheel robot :)
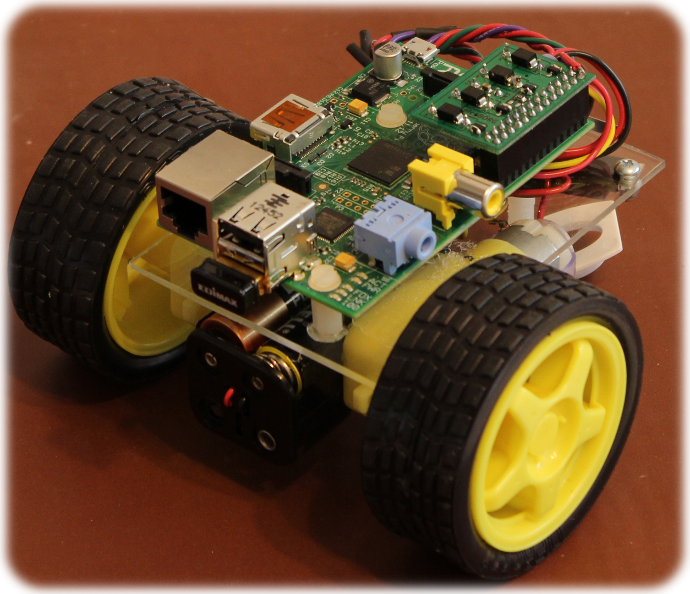
The first thing to do then is to build a robot with two motorised wheels and a caster wheel (like you get on shopping trolleys) or a runner (a smooth surface intended to glide on another surface).
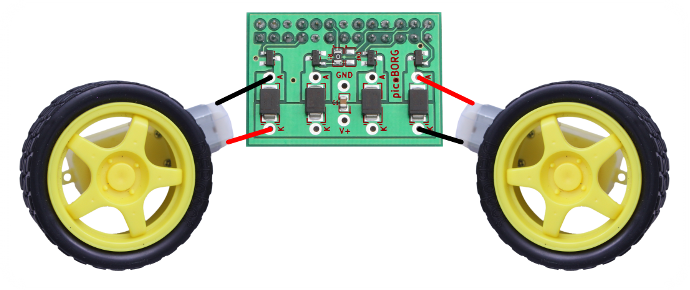 When connecting up the PicoBorg the connections should be:
When connecting up the PicoBorg the connections should be:
Now we need the scripts.
RemoteKeyBorg is a script that comes in two parts:
and you can download the RemoteKeyBorgC script file as text here.
Save the text files on your Raspberry Pis as RemoteKeyBorgS.py and RemoteKeyBorgC.py respectively.
Make the scripts executable using
and run on the Raspberry Pi with the PicoBorg using
and run on the commanding Raspberry Pi using
RemoteKeyBorg is a pair of scripts that allow a Raspberry Pi with a PicoBorg to expose itself on the network and another to command it.
This example is intended to demonstrate using the keyboard left, up, and right keys to control a three wheel robot :)

The first thing to do then is to build a robot with two motorised wheels and a caster wheel (like you get on shopping trolleys) or a runner (a smooth surface intended to glide on another surface).
 When connecting up the PicoBorg the connections should be:
When connecting up the PicoBorg the connections should be:- Left motor connected to drive #1, wired +/+, -/-
- Right motor connected to drive #4, wired +/-, -/+
Now we need the scripts.
RemoteKeyBorg is a script that comes in two parts:
- RemoteKeyBorgS.py (Server)
This script runs on the Raspberry Pi with the PicoBorg and sets the PicoBorg drives when told to
For remote control we suggest this Raspberry Pi is connected to the network using WiFi, so it is free of cables :) - RemoteKeyBorgC.py (Client)
This script runs on the Raspberry Pi which is controlling the robot, it loads a blank window which responds to up, left and right
This script can be run on any computer connected to the same network, running Python and pygame, but it needs a GUI available (no telnets I am afraid...)
If testing this may even be run on the same Raspberry Pi, but that would defeat the point :)
broadcastIPin RemoteKeyBorgC.py, line 10
IP address to send to (Raspberry Pi with the PicoBorg), may be a single machine (e.g. 192.168.1.5) or a broadcast (e.g. 192.168.1.255) where '255' is used to indicate that number is everybodybroadcastPortin RemoteKeyBorgC.py, line 11
Number used to identify who gets network messages, if two copies of RemoteKeyBorg are used in the same network this should be changed to identify which copy is whichleftDrivein RemoteKeyBorgC.py, line 12
Drive number for the left wheel, change this if your wiring does not match the example diagramrightDrivein RemoteKeyBorgC.py, line 13
Drive number for the right wheel, change this if your wiring does not match the example diagramintervalin RemoteKeyBorgC.py, line 14
Delay between checking for keyboard updates, smaller numbers respond faster but will use more processor timeregularUpdatein RemoteKeyBorgC.py, line 15
Set to True the script will send a command at every interval, set to False it will only send a command when a key changesportListenin RemoteKeyBorgS.py, line 32
If you change the port your RemoteKeyBorgC.py is using, change this to match
and you can download the RemoteKeyBorgC script file as text here.
Save the text files on your Raspberry Pis as RemoteKeyBorgS.py and RemoteKeyBorgC.py respectively.
Make the scripts executable using
chmod +x RemoteKeyBorg*.pyand run on the Raspberry Pi with the PicoBorg using
sudo ./RemoteKeyBorgS.pyand run on the commanding Raspberry Pi using
./RemoteKeyBorgC.pyRemoteKeyBorgS
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: Latin-1
# Load library functions we want
import SocketServer
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
# Set which GPIO pins the drive outputs are connected to
DRIVE_1 = 4
DRIVE_2 = 18
DRIVE_3 = 8
DRIVE_4 = 7
# Set all of the drive pins as output pins
GPIO.setup(DRIVE_1, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(DRIVE_2, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(DRIVE_3, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(DRIVE_4, GPIO.OUT)
# Map of drives to pins
lDrives = [DRIVE_1, DRIVE_2, DRIVE_3, DRIVE_4]
# Function to set all drives off
def MotorOff():
GPIO.output(DRIVE_1, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(DRIVE_2, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(DRIVE_3, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(DRIVE_4, GPIO.LOW)
# Settings for the RemoteKeyBorg server
portListen = 9038 # What messages to listen for (LEDB on an LCD)
# Class used to handle UDP messages
class PicoBorgHandler(SocketServer.BaseRequestHandler):
# Function called when a new message has been received
def handle(self):
global isRunning
request, socket = self.request # Read who spoke to us and what they said
request = request.upper() # Convert command to upper case
driveCommands = request.split(',') # Separate the command into individual drives
if len(driveCommands) == 1:
# Special commands
if request == 'ALLOFF':
# Turn all drives off
MotorOff()
print 'All drives off'
elif request == 'EXIT':
# Exit the program
isRunning = False
else:
# Unknown command
print 'Special command "%s" not recognised' % (request)
elif len(driveCommands) == len(lDrives):
# For each drive we check the command
for driveNo in range(len(driveCommands)):
command = driveCommands[driveNo]
if command == 'ON':
# Set drive on
GPIO.output(lDrives[driveNo], GPIO.HIGH)
elif command == 'OFF':
# Set drive off
GPIO.output(lDrives[driveNo], GPIO.LOW)
elif command == 'X':
# No command for this drive
pass
else:
# Unknown command
print 'Drive %d command "%s" not recognised!' % (driveNo, command)
else:
# Did not get the right number of drive commands
print 'Command "%s" did not have %d parts!' % (request, len(lDrives))
try:
global isRunning
# Start by turning all drives off
MotorOff()
raw_input('You can now turn on the power, press ENTER to continue')
# Setup the UDP listener
remoteKeyBorgServer = SocketServer.UDPServer(('', portListen), PicoBorgHandler)
# Loop until terminated remotely
isRunning = True
while isRunning:
remoteKeyBorgServer.handle_request()
# Turn off the drives and release the GPIO pins
print 'Finished'
MotorOff()
raw_input('Turn the power off now, press ENTER to continue')
GPIO.cleanup()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# CTRL+C exit, turn off the drives and release the GPIO pins
print 'Terminated'
MotorOff()
raw_input('Turn the power off now, press ENTER to continue')
GPIO.cleanup()
RemoteKeyBorgC
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: Latin-1
# Load library functions we want
import socket
import time
import pygame
# Settings for the RemoteKeyBorg client
broadcastIP = '192.168.0.255' # IP address to send to, 255 in one or more positions is a broadcast / wild-card
broadcastPort = 9038 # What message number to send with (LEDB on an LCD)
leftDrive = 1 # Drive number for left motor
rightDrive = 4 # Drive number for right motor
interval = 0.1 # Time between keyboard updates in seconds, smaller responds faster but uses more processor time
regularUpdate = True # If True we send a command at a regular interval, if False we only send commands when keys are pressed or released
# Setup the connection for sending on
sender = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM, socket.IPPROTO_UDP) # Create the socket
sender.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_BROADCAST, 1) # Enable broadcasting (sending to many IPs based on wild-cards)
sender.bind(('0.0.0.0', 0)) # Set the IP and port number to use locally, IP 0.0.0.0 means all connections and port 0 means assign a number for us (do not care)
# Setup pygame and key states
global hadEvent
global moveUp
global moveDown
global moveLeft
global moveRighte
global moveQuit
hadEvent = True
moveUp = False
moveDown = False
moveLeft = False
moveRight = False
moveQuit = False
pygame.init()
screen = pygame.display.set_mode([300,300])
pygame.display.set_caption("RemoteKeyBorg - Press [ESC] to quit")
# Function to handle pygame events
def PygameHandler(events):
# Variables accessible outside this function
global hadEvent
global moveUp
global moveDown
global moveLeft
global moveRight
global moveQuit
# Handle each event individually
for event in events:
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
# User exit
hadEvent = True
moveQuit = True
elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:
# A key has been pressed, see if it is one we want
hadEvent = True
if event.key == pygame.K_UP:
moveUp = True
elif event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:
moveDown = True
elif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:
moveLeft = True
elif event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:
moveRight = True
elif event.key == pygame.K_ESCAPE:
moveQuit = True
elif event.type == pygame.KEYUP:
# A key has been released, see if it is one we want
hadEvent = True
if event.key == pygame.K_UP:
moveUp = False
elif event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:
moveDown = False
elif event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:
moveLeft = False
elif event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:
moveRight = False
elif event.key == pygame.K_ESCAPE:
moveQuit = False
try:
print 'Press [ESC] to quit'
# Loop indefinitely
while True:
# Get the currently pressed keys on the keyboard
PygameHandler(pygame.event.get())
if hadEvent or regularUpdate:
# Keys have changed, generate the command list based on keys
hadEvent = False
driveCommands = ['X', 'X', 'X', 'X'] # Default to do not change
if moveQuit:
break
elif moveLeft:
driveCommands[leftDrive - 1] = 'OFF'
driveCommands[rightDrive - 1] = 'ON'
elif moveRight:
driveCommands[leftDrive - 1] = 'ON'
driveCommands[rightDrive - 1] = 'OFF'
elif moveUp:
driveCommands[leftDrive - 1] = 'ON'
driveCommands[rightDrive - 1] = 'ON'
else:
# None of our expected keys, stop
driveCommands[leftDrive - 1] = 'OFF'
driveCommands[rightDrive - 1] = 'OFF'
# Send the drive commands
command = ''
for driveCommand in driveCommands:
command += driveCommand + ','
command = command[:-1] # Strip the trailing comma
sender.sendto(command, (broadcastIP, broadcastPort))
# Wait for the interval period
time.sleep(interval)
# Inform the server to stop
sender.sendto('ALLOFF', (broadcastIP, broadcastPort))
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# CTRL+C exit, inform the server to stop
sender.sendto('ALLOFF', (broadcastIP, broadcastPort))